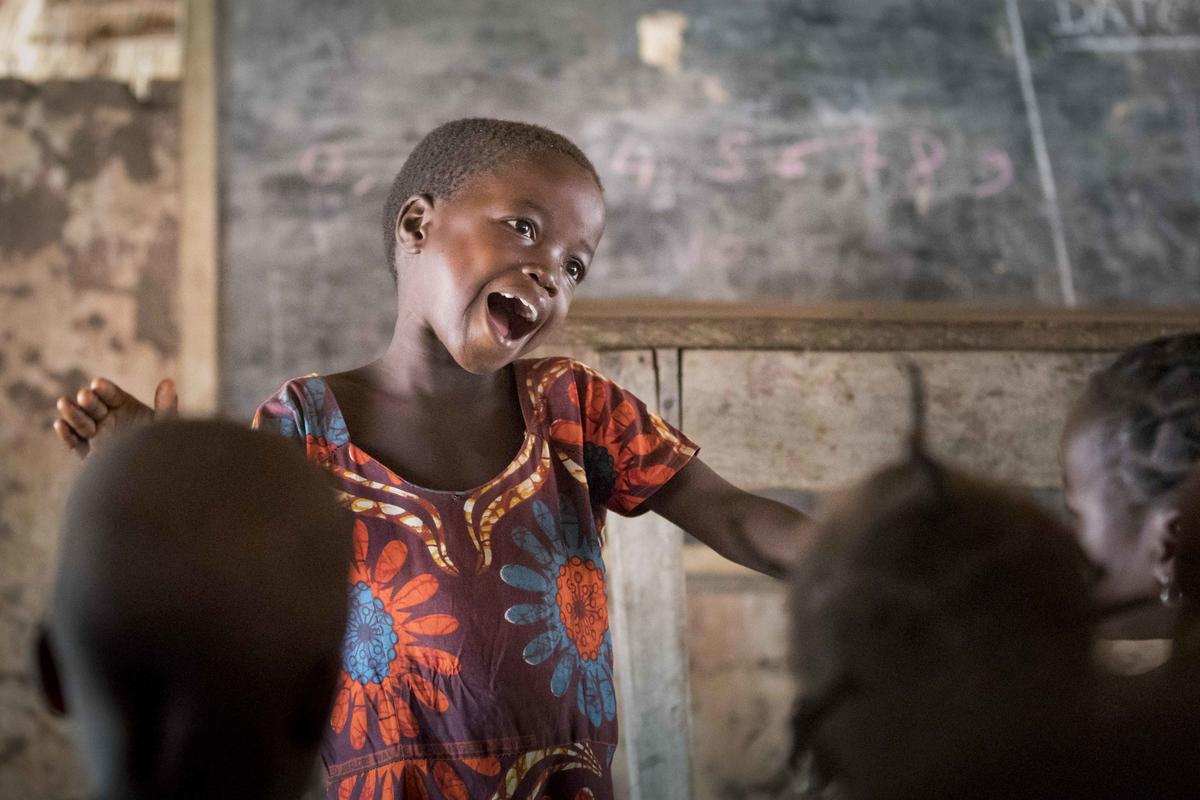Four million refugee children go without schooling: UNHCR report

Four million refugee children go without schooling: UNHCR report
While the population uprooted by wars and persecution is on the rise worldwide, the numbers of refugee children enrolled in schools is failing to keep pace, according to a new report by UNHCR, the UN Refugee Agency released today.
The study, Turn the Tide: Refugee Education in Crisis, found that four million refugee children do not attend school, an increase of half a million of out-of-school refugee children in just one year.
By the end of 2017, there were more than 25.4 million refugees around the world, 19.9 million of them under UNHCR’s mandate. More than half – 52 per cent – were children. Among them, 7.4 million were of school age.
“Education is a way to help children heal, but it is also key to rebuilding their countries,” said Filippo Grandi, UN High Commissioner for Refugees. “Without education, the future of these children and their communities will be irrevocably damaged.”
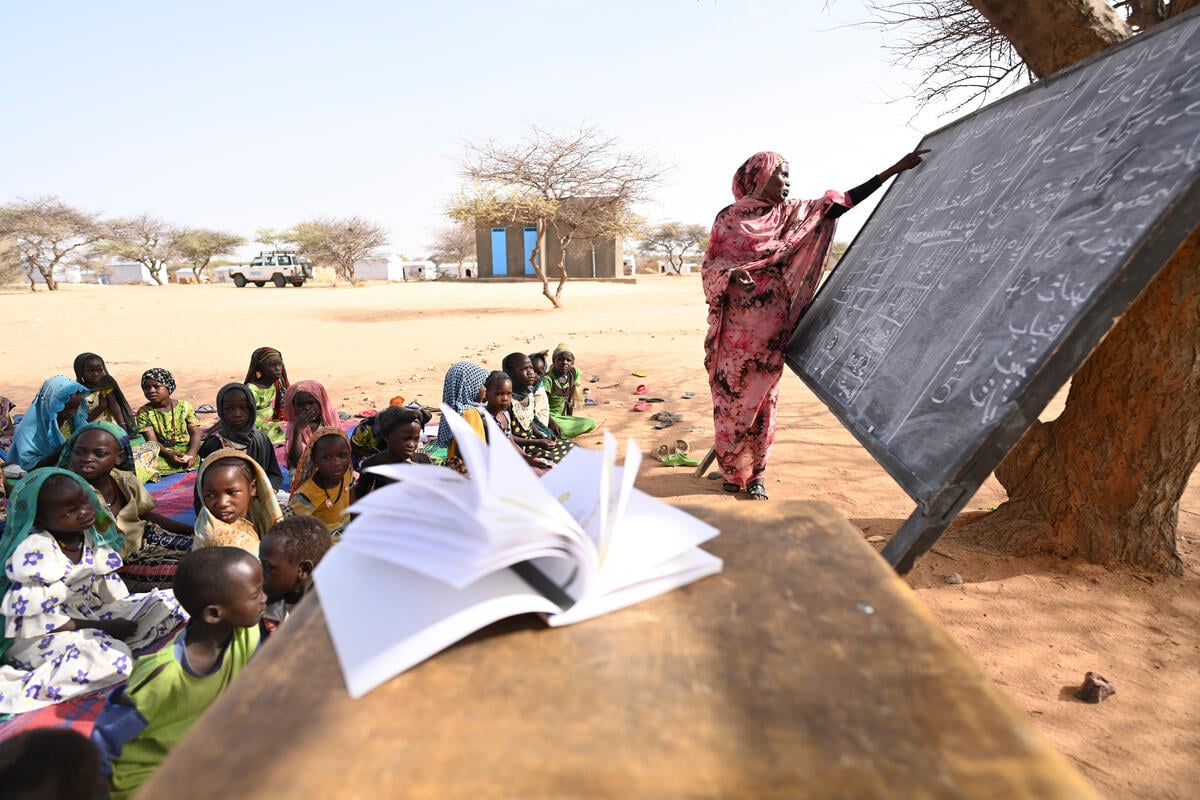
Only 61 per cent of refugee children attend primary school, compared to 92 per cent of children globally.
“Education is a way to help children heal, but it is also key to rebuilding their countries.”
As refugee children get older, this gap grows. Nearly two thirds of refugee children who go to primary school do not make it to secondary school. In total, 23 per cent of refugee children attend secondary school, compared to 84 per cent of children globally.
At tertiary level, the gap becomes a chasm. Globally, enrolment in higher education stands at 37 per cent, while only one per cent of refugees have the same opportunity – a figure that has not changed in three years.
“School is the first place in months or even years where refugee children find any normality,” adds Grandi. “Based on current patterns, unless urgent investment is undertaken, hundreds of thousands more children will join these disturbing statistics.”
The report highlights progress made by those committed to the New York Declaration for Refugees and Migrants in enrolling an additional 500,000 formerly out-of-school refugee children in 2017. At the same time, it calls for more to be done to ensure all refugees get the quality education they deserve.
The report urges host countries to enrol refugee children in national systems, with a proper curriculum, all the way through primary and secondary school, to allow for recognized qualifications that can be their springboard to university or higher vocational training.
It further notes that countries in developing regions host 92 per cent of the world’s school-age refugees and need more sustained financial support from the international community.
Finally, the report calls for stronger partnerships with the private sector, humanitarian and development organizations and governments to increase sustainable solutions for refugee education.
Read a news release on the report here.