Mar 27, 2023
Data in humanitarian action can provide accurate and up-to-date information on the location, size, demographics and needs of populations affected by crises. This information is used to develop and implement targeted interventions, such as the provision of water, sanitation, shelter, and other critical emergency assistance to those who need it most.

Mar 2, 2023
At the heart of the JDC’s efforts, we are supporting policy change informed by research using high-quality data gathered according to recognized standards and definitions.

Feb 16, 2023
The pathway towards the inclusion of refugees, IDPs, and stateless persons in national systems starts with mainstreaming them into national statistics exercises. But more is needed. Experience shows these populations need champions to ensure their inclusion in national development plans.

Feb 3, 2023
There is scope for improving the targeting of refugee child poverty, with potentially substantial gains in children’s wellbeing, if data exercises are designed to allow for intra-household poverty calculations.
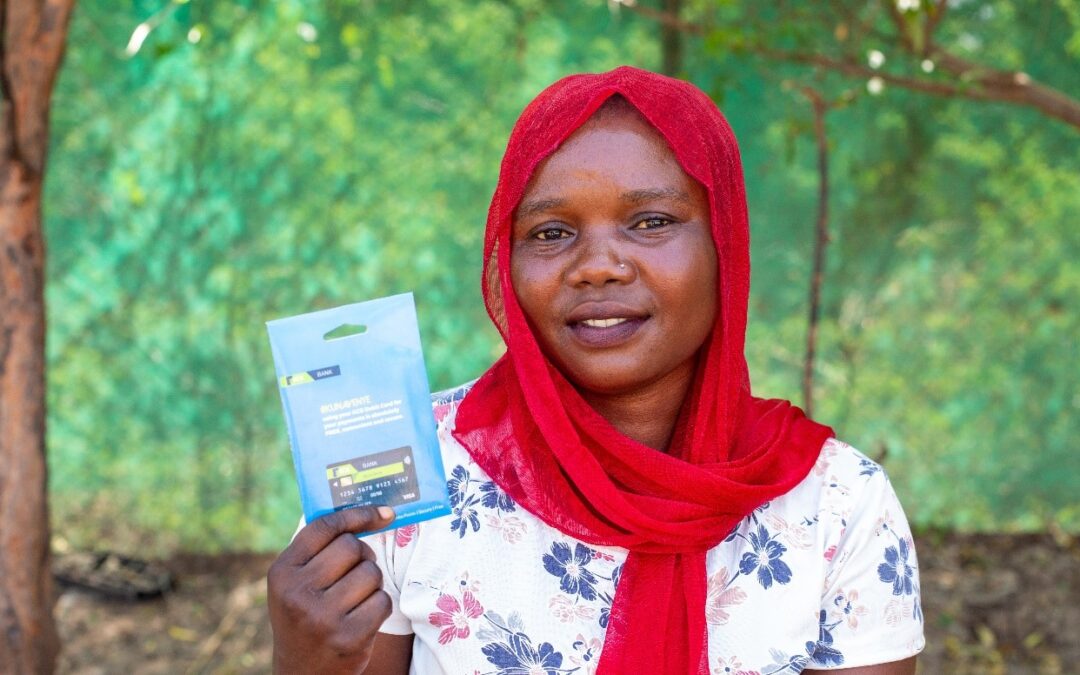

Jan 12, 2023
Refugees’ financial needs evolve over time. Access to affordable and useful financial services ena-bles their socioeconomic inclusion and helps them better plan for their future.
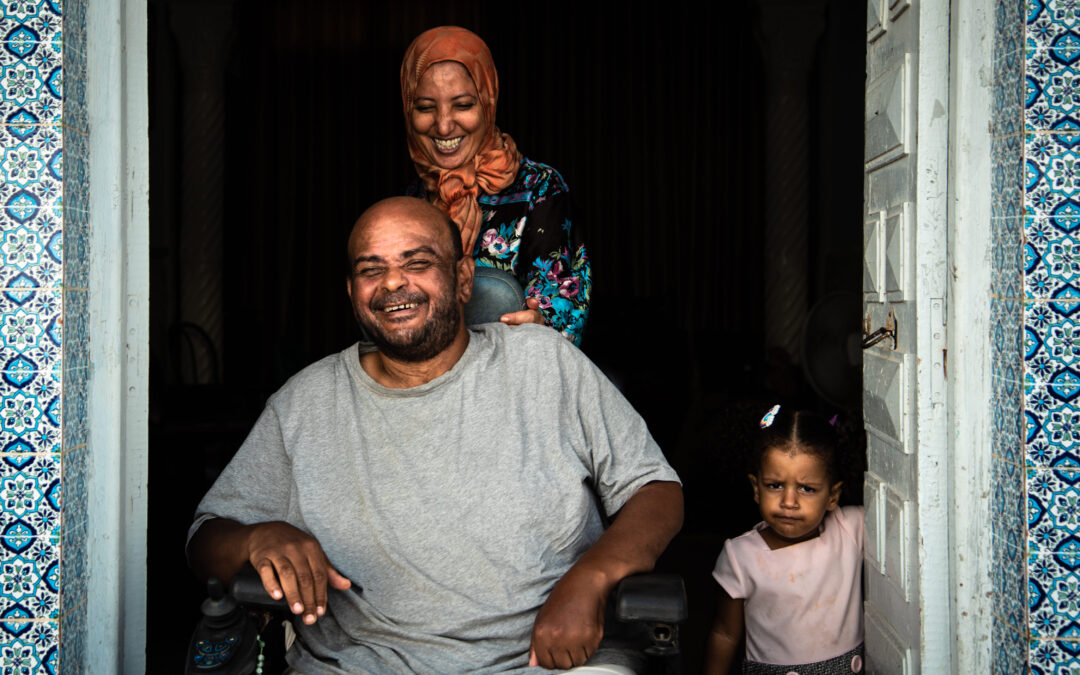

Dec 7, 2022
To include refugees sustainably and effectively, there must be a well-supported health system capable of meeting the needs of refugees and host communities.
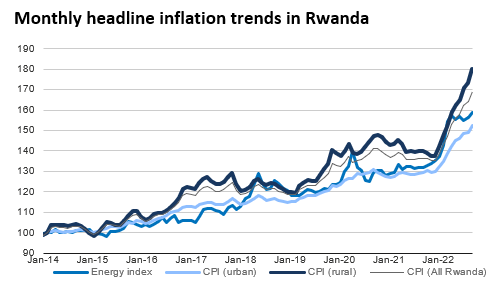
Nov 17, 2022
A shock-responsive assistance distribution system that allows for adjustments of assistance could be more effective in helping refugee communities cope with changes in the wider economy.
Nov 9, 2022
Reliable data is essential when planning appropriate solutions for refugees and surrounding communities. Data gaps are potential obstacles when advocating for the involvement of development partners to invest in effective programmes.
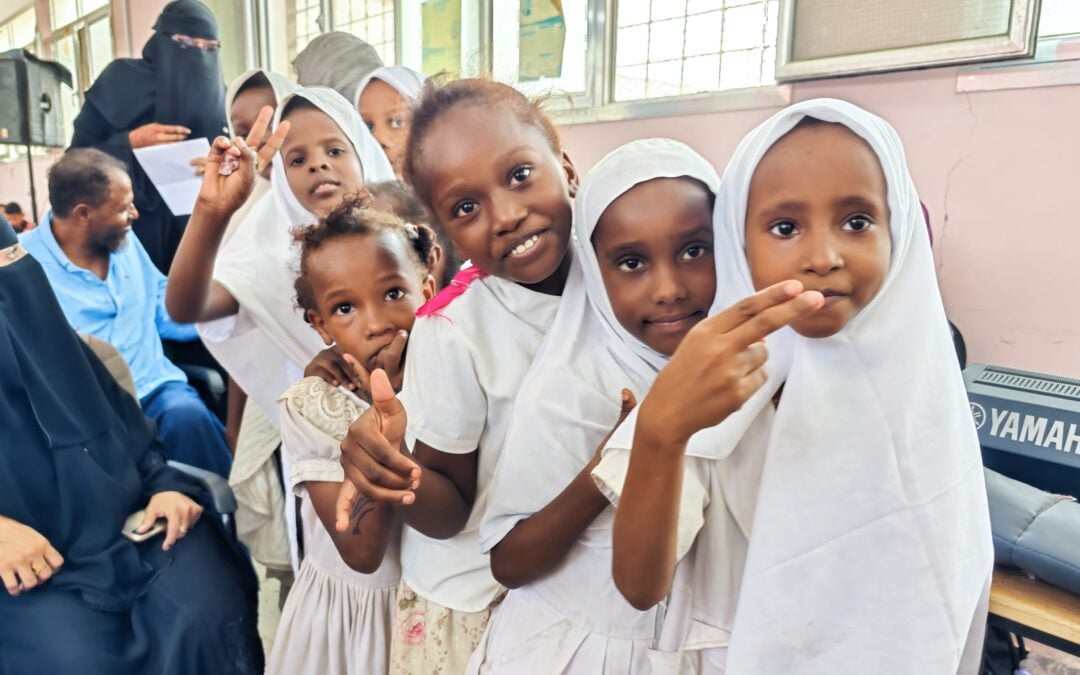

Oct 27, 2022
While in the past emphasis lay on camps serviced by humanitarian actors, we now know that inclusion of refugees, IDPs, and stateless people in the hosting context is not only a good option, but a necessity to achieve better protection outcomes and to lay the ground for solutions.
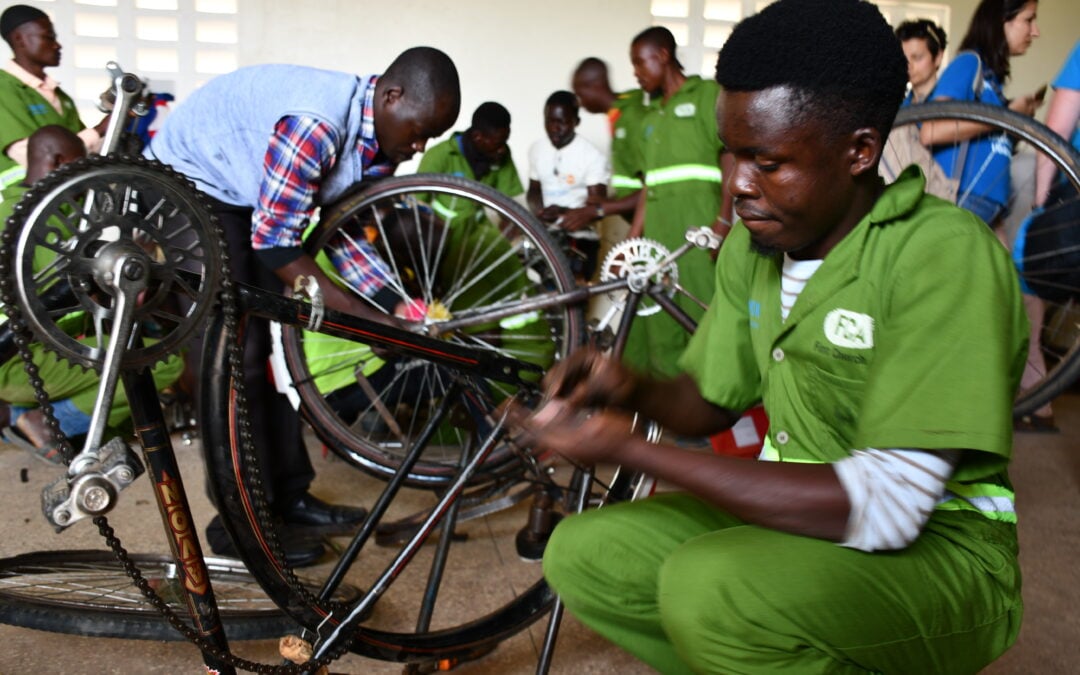

Sep 8, 2022
A UNHCR study in Uganda proposes stronger action linking youth to the labour market, among other policy steps to improve outcomes for refugees and Ugandan host communities.